Fano resonance
In physics, a Fano resonance is a type of resonant scattering phenomenon that gives rise to an asymmetric line-shape. Interference between a background and a resonant scattering process produces the asymmetric line-shape. It is named after Italian physicist Ugo Fano who gave a theoretical explanation for the scattering line-shape of inelastic scattering of electrons off of helium[1][2]. However Ettore Majorana was the first to discover this phenomenon[3]. Because it is a general wave phenomenon, examples can be found across many areas of physics and engineering.
Contents |
History
The explanation of the Fano line-shape first appeared in the context of inelastic electron scattering by helium and autoionization. The incident electron doubly excites the atom to the 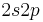 state. The doubly excited atom spontaneously decays by ejecting one of the excited electrons. Fano showed that interference between the amplitude to simply scatter the incident electron and the amplitude to scatter via autoionization creates an asymmetric scattering line-shape around the autoionization energy with a line-width very close to the inverse of the autoionization lifetime.
state. The doubly excited atom spontaneously decays by ejecting one of the excited electrons. Fano showed that interference between the amplitude to simply scatter the incident electron and the amplitude to scatter via autoionization creates an asymmetric scattering line-shape around the autoionization energy with a line-width very close to the inverse of the autoionization lifetime.
Explanation
The Fano resonance line-shape is due to interference between two scattering amplitudes, one due to scattering within a continuum of states (the background process) and the second due to a excitation of a discrete state (the resonant process). The energy of the resonant state must lie in the energy range of the continuum (background) states for the effect to occur. Near the resonant energy, the background scattering amplitude typical varies slowly with energy while the resonant scattering amplitude changes both in magnitude and phase quickly. It is this variation that creates the asymmetric profile.
For energies far from the resonant energy the background scattering process dominates. Within 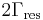 of the resonant energy, the phase of the resonant scattering amplitude changes by
of the resonant energy, the phase of the resonant scattering amplitude changes by 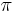 . It is this rapid variation in phase that creates the asymmetric line-shape.
. It is this rapid variation in phase that creates the asymmetric line-shape.
Fano showed that the total scattering cross-section assumes the following form,
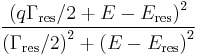
where q, the Fano parameter, measures the ratio of resonant scattering to the direct (background) scattering amplitude. (This is consistent with the interpretation within the Feshbach–Fano partitioning theory.) In the case the direct scattering amplitude vanishes, the q parameter becomes infinite and the Fano formula boils down to the usual Breit–Wigner (Lorentzian) formula:
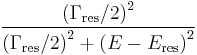
Examples
Examples of Fano resonances can be found in atomic physics, nuclear physics, condensed matter physics, circuits, microwave engineering, nonlinear optics and nanophotonics.
References
- ^ “ A. Bianconi Ugo Fano and shape resonances in X-ray and Inner Shell Processes” AIP Conference Proceedings (2002): (19th Int. Conference Roma June 24–28, 2002) A. Bianconi arXiv: cond-mat/0211452 21 November 2002
- ^ Ugo Fano (1961) "Effects of Configuration Interaction on Intensities and Phase Shifts," Phys. Rev. 124, pp. 1866–1878 doi:10.1103/PhysRev.124.1866
- ^ Alessandra Vittorini-Orgeas, Antonio Bianconi "From Majorana Theory of Atomic Autoionization to Feshbach Resonances in High Temperature Superconductors" Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 22, 215-221 (2009)